Solutions
Continuous Delivery Pipeline Automation Tools
Scale Continuous Delivery across all applications, change events and environments with Chef.

Continuous Delivery Tools for Every Team, Every Change, and Every Environment
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a set of capabilities that enables application and DevOps teams to get changes of all types into production quickly, safely and reliably. Through the use of pipelines, organizations can define a consistent path to production where changes can be peer reviewed, automatically tested, and audited as they make their way to production.
CD goes beyond application code changes automating not only the continuous integration of the software but also the delivery of infrastructure, supporting systems and requirements for running and maintaining the application. Successful Continuous Delivery requires not only the successful automated delivery of an application but also:
How Chef Fits in Continuous Delivery Pipelines
Most organizations already have a source control, build server, and technology provisioning process. Chef doesn't replace these tools but makes them easier to manage, scale and validate. For example, tools like Jenkins require users to create and maintain individual pipelines for each application. Chef creates universal, compliant artifacts that can be consumed by any pipeline automation tool (Jenkins, Azure DevOps, Build kite, etc.), deployed to almost any environment (Windows, Linux, Docker, Cloud Platforms, Kubernetes, VMware, etc.) and validated in real-time.
Benefits to Chef’s Approach to Continuous Delivery
Drive Consistency Across Dev, Ops and Security Teams
Consistently and securely deliver across all teams, change events and environments.
Reduce Tool and Script Sprawl
Minimize the number of tools and custom scripts that need to be maintained.
Align Delivery Processes
Use the same process to package all apps and create a single app directory.
Stop the Accrual of Technical Debt
Replace manual runbooks with codified and searchable artifacts for all apps and dependencies.
A Consistent and Scalable Approach to Continuous Delivery
Chef enables IT teams to scale Continuous Delivery across applications and all change events by providing a consistent way to define, package and deliver applications, infrastructure and compliance policies into secure coded artifacts that can be consumed by any pipeline automation system. Best of all, Chef’s approach is technology and environment agnostic. Chef’s solution can be used across operating systems, development languages and run-time environments on-premises or in the cloud without any rewriting or refactoring. Chef helps teams define “everything” an application needs to be built, run and managed independent of any underlying infrastructure.
Learn more about Application Definition
Chef’s Continuous Delivery Solution
Continuous Delivery at scale requires consistent patterns that are not tool- and platform-specific. Chef applies an “as code” approach to the entire technology stack to enable consistent delivery patterns when working with legacy, cloud-native and everything in between. Chef’s approach includes policy along with the release, and tests are run and errors are addressed at build time vs. run time. Each policy and dependency is defined as code, versioned, and stored in source control along with the application code. They travel the pipeline along with the application code, are updated and versioned along with the application and monitored in production.
Chef Continuous Delivery Framework

Define and Package applications, infrastructure, and compliance policies across technologies using a common approach.

Integrate with preferred source control, build, infrastructure provisioning, secrets management and other tools.
Deliver to any environment, validate status and remediate in real-time.
Getting rid of our homegrown tools and replacing them with Habitat made a huge difference in terms of consistency, reliability and visibility.
Inherent Pipeline Security and Compliance with Chef
Attaching codified assets to an application release at the source control level is the easiest, cheapest and fastest way to ensure compliance and accelerate delivery. Chef embeds security testing and remediation in the entire delivery process and deeply understands dependencies so teams can correct issues as early as possible, make changes confidently, and gain real-time visibility into risk. All Chef published artifacts are stored in a single-origin that can not be accessed by humans, ensuring they are immutable. Responsible teams know the status of every release along with how the release was configured and who configured it.
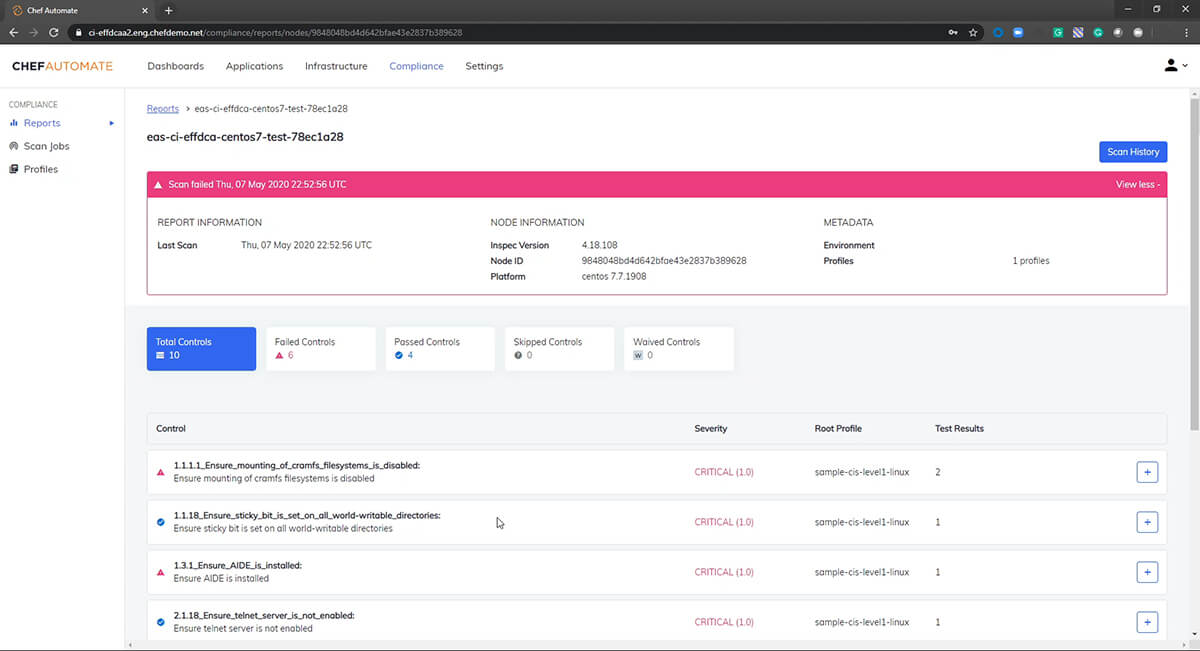
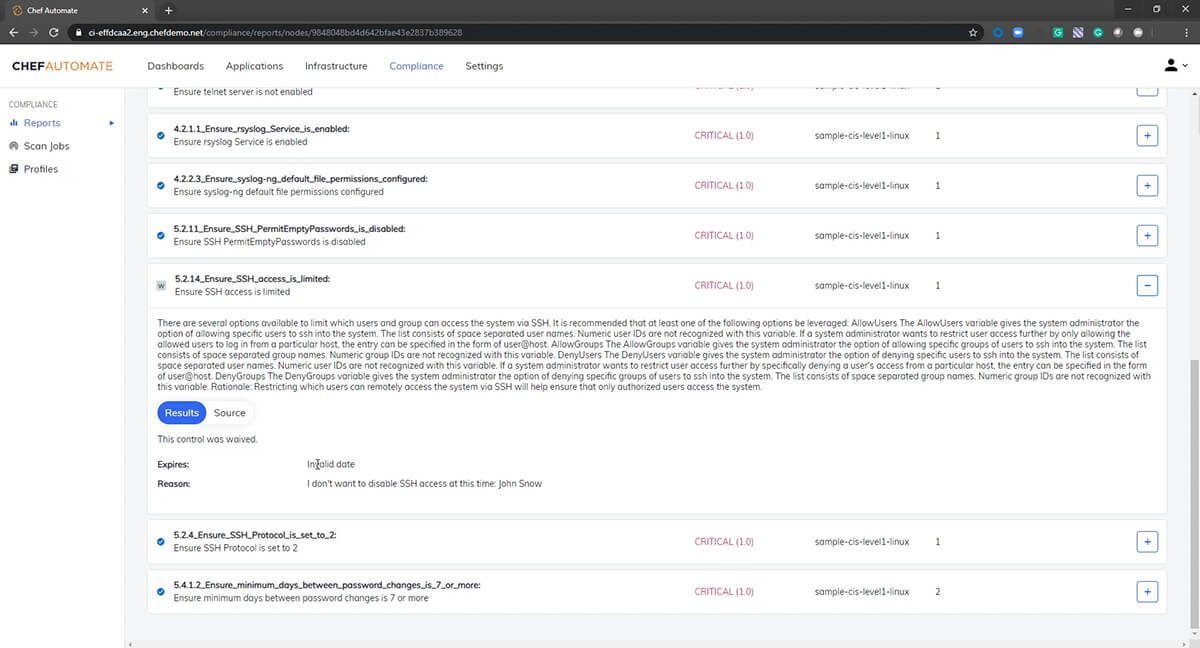
Chef Compliance further simplifies the security of pipelines by providing standards-based audit and remediation content. Chef Compliance helps security and operations teams maintain complete visibility over the compliance status of their estate, while closing the loop between audit and remediation to enable continuous compliance in the enterprise. It comes with extensive audit and remediation content based on CIS benchmarks and DISA-STIGs out of the box that can be easily tuned to meet specific needs of every organization.
Chef Enterprise Automation Stack: Secure Continuous Delivery for Applications and Infrastructure
Chef Enterprise Automation Stack (EAS) is an automation platform for DevSecOps teams to build, deploy, manage, and secure any application running on any infrastructure. The Chef Enterprise Stack includes the following Chef projects:
Chef Automate
Enterprise dashboard and analytics tool enabling cross-team collaboration with actionable insights for configuration and compliance and an auditable history of changes to environments.
Learn More About Chef AutomateChef Habitat
Automation capabilities for defining application build-time and run-time requirements, packaging and delivering applications to almost any environment regardless of operating system or platform.
Learn More About Chef HabitatChef Inspec
Automation capabilities to define and continuously test and enforce security and compliance standards on-prem and in the cloud.
Learn More About Chef InspecChef Infra
Infrastructure automation capabilities to configure and remediate any number of systems across desktop, cloud and private data center environments.
Learn More About Chef InfraRecommended Content



Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Continuous Delivery Pipeline?
A Continuous Delivery Pipeline (CDP) is a series of automated processes designed to deliver new software efficiently and reliably. Continuous Delivery leverages a combination of tools, processes, and a cultural change toward deep collaboration. It enables DevOps teams to make software changes and get them into production quickly, reliably, safely and (nearly) continuously.
This Continuous Delivery depends on pipelines where the software changes are by peers, tested automatically and audited before being released into the production environment.
What is a Continuous Delivery Pipeline in SAFe?
In the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), a Continuous Delivery Pipeline (CDP) is a key element that represents the workflows, activities and automation needed to move new functionality from ideation to release. The SAFe pipeline is based on four elements:
- Continuous exploration
- Continuous integration
- Continuous deployment
- Release on demand
DevOps teams can map their existing approaches to the SAFe pipeline and benefit from this higher-level approach, such as internal (within DevOps) and external (with customers and users) feedback loops.
What are the principles of the Continuous Delivery Pipeline?
The principles of a Continuous Delivery Pipeline (CDP) are designed to maintain efficient, reliable and high-quality software delivery. Here are some key principles that drive Continuous Delivery Pipelines:
- Automating the Software Delivery Pipeline
- Maintaining a Reliable and Consistent Codebase
- Extensive Test Automation
- Collaborative Development and Continuous Feedback
In addition to adhering to these principles, Continuous Delivery Pipelines should help DevOps teams apply agile principles to all the software, software components and infrastructure that drive agile enterprise CI/CD pipelines.
What is the difference between Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)?
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are crucial practices in modern software development, but they serve different purposes.
Continuous Integration focuses on integrating code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository frequently, often several times daily. Each integration is verified by an automated build and automated tests to detect integration errors as quickly as possible. The main goal is to provide rapid feedback so that if a defect is introduced into the codebase, it can be identified and corrected promptly.
Continuous Delivery takes the output from CI and ensures that it can be released to production at any time. This involves deploying code changes to a staging environment and running additional automated tests to ensure the software works as expected in a production-like setting. The primary goal is to have a codebase that is always deployable, allowing for frequent and reliable releases to production.
In summary, while CI involves integrating and testing code frequently to catch issues early, CD involves ensuring that the code is always ready to be deployed to production, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
What are the elements of a Continuous Delivery Pipeline (CDP)?
A Continuous Delivery Pipeline (CDP) is comprised of several essential components that collaborate to ensure the efficient and reliable delivery of software. The primary elements are as follows:
- Continuous Exploration: This phase focuses on identifying what needs to be developed by analyzing market demands and customer requirements. Key activities include market research, gathering customer feedback, and validating hypotheses.
- Continuous Integration: Code changes are regularly integrated into a shared repository in this stage. Automated builds and tests are conducted to detect potential issues early, ensuring that the codebase remains in a deployable condition.
- Continuous Deployment: This phase involves the automated deployment of code changes to a staging environment and, if necessary, to production. It ensures that software can be released with minimal manual intervention, maintaining readiness for deployment at any time.
- Release on Demand: The final phase grants the flexibility to release new features to users as required. This approach allows software releases to be aligned with market demands and business objectives.
Together, these components enable organizations to deliver high-quality software quickly and predictably, thereby enhancing business agility and customer satisfaction.